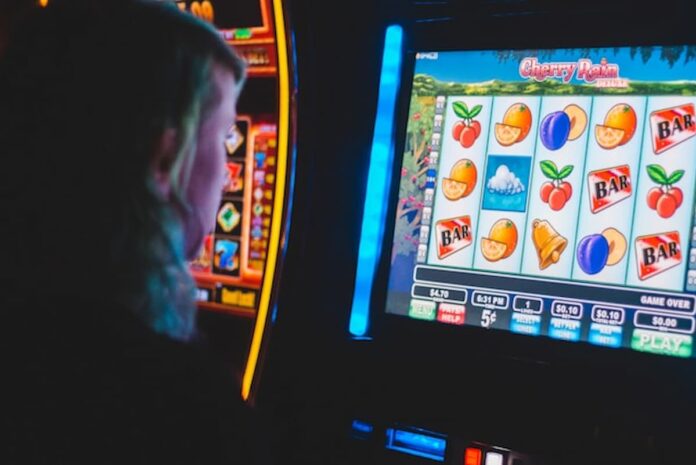
An incident at a Henry County gas station has reignited the debate over “skill game” machines in Virginia, highlighting the state’s failure to resolve the status of the controversial devices.
Gas Station Break-In Sparks Alarm
According to the Henry County Sheriff’s Office, on September 27, 41-year-old Thornton Burnette tried to break into a skill game terminal at J&H Market in Martinsville after losing money on the terminal earlier.
Burnette had a firearm strapped around his neck while he allegedly attempted to break into the machine with a power tool. He caused roughly $1,000 in damage.
Authorities arrested Burnette two days later. He now faces multiple charges, including attempted robbery, destruction of property, and firearm offenses. He remains in custody without bond, with a court appearance scheduled for December.
In a statement shared by local media outlet WSET, the Henry County Sheriff’s Office stated that it had not previously been aware of a gambling room at the gas station.
“The incident occurred in a room that appeared to be used for illegal gambling. The Henry County Sheriff’s Office was previously unaware of the existence of this gambling room or the gaming machines. That matter is ongoing and still under investigation.”
State Delegate Wendell Walker, responding to the news, suggested the issue highlights broader tensions over gambling competition. Some view the unregulated machines as cannibalizing the newly established and growing casino sector in Virginia.
Skill Games in the Gray Zone
Skill games resemble slot machines visually. However, manufacturers claim skill games involve an element of player decision-making, such as memory or pattern recognition. That, they argue, separates them from the definition of a gambling device. Meanwhile, opponents say that they functionally operate like slot machines.
Due to this ambiguity, skill games often exist in a legal gray area across North America. In most states, they’re unregulated and don’t contribute to state tax revenue. Only a handful, such as Nebraska, which taxes the terminals 5% on revenue, have chosen the regulatory path.
Skill games are not only a US issue. Last month, in Ontario, a judge ruled that specific skill game machines are illegal under the law. Since then, the Alcohol and Gaming Commission of Ontario has intensified enforcement by seizing skill game terminals throughout the province.
Virginia’s Legal Tug-of-War
The debate over skill game machines has been ongoing in Virginia for several years.
Early Ban & Court Battles
In 2020, Virginia lawmakers passed a bill to ban skill games. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the ban didn’t go into effect until the following year.
Operators and manufacturers challenged the ban in court, allowing the machines to continue operating. The fight culminated in October 2023, when the Virginia Supreme Court ruled the state’s ban constitutional and reinstated full enforcement.
Attempts at Legalization
In 2024, Virginia was on the verge of legalizing and regulating skill game terminals. The General Assembly passed a bill to regulate the machines with a 25% tax rate and oversight by the Virginia Lottery.
However, Governor Glenn Youngkin vetoed the bill. He argued that it lacked safeguards and could lead to the unchecked expansion of gambling. Youngkin offered amendments, which lawmakers declined. That left the 2020 ban in place.
Loopholes & Local Rulings
As judges in a few states, such as Tennessee, have ruled against specific skill game terminals, manufacturers have introduced “redeveloped” machines in an attempt to circumvent the law.
Earlier this year, the skill game debate in Virginia took an unexpected turn after a county judge ruled that the Queen of Virginia (QVS2) games by Pace-O-Matic do not meet the legal definition of an illegal gambling device.
Judge Hugh Campbell of the Hanover County General District Court’s decision was based on the fact that the redeveloped machines do not require players to insert coins, bills, or tokens to play.
The judge also found that the state gambling statute’s definition is too vague. This makes it difficult for business owners to comply with the law.
The decision gave operators fresh momentum, even as the Supreme Court’s 2023 ruling remains the overarching precedent.
Lawmakers Still Split
A new proposal to regulate skill game terminals appeared in the Virginia legislature earlier this year. Senate Democrats floated a budget amendment that would legalize and tax skill games with a 25% gross receipts levy.
The proposal did not make its way into the final budget. Still, supporters continue to lobby for regulation. They argue the state is losing millions in potential revenue.
Opponents, including casino operators and some lawmakers, counter that leaving the ban intact prevents the proliferation of unregulated gambling and related crime.